
PHONE REPAIRS
Objectives
Technical Competence: To equip students with the technical skills and knowledge required to diagnose and repair various types of mobile phones, including hardware and software issues.
Safety Awareness: To instill a strong sense of safety practices, ensuring that students understand the potential risks associated with phone repair and how to mitigate them.
Understanding Mobile Technology: To provide a comprehensive understanding of mobile phone technology, components, and how they function.
Troubleshooting Skills: To develop the ability to identify and troubleshoot common problems and issues in mobile phones systematically.
Component Identification: To teach students how to identify and understand the various components within a mobile phone, such as motherboards, screens, batteries, and connectors.
Software Repair: To train students in resolving software-related issues, including operating system problems, firmware updates, and data recovery.
Customer Service Skills: To instill effective communication and customer service skills, as phone repair often involves dealing with customers who are frustrated or concerned about their devices.
Business Skills: To educate students about the business aspects of phone repair, including setting up a repair shop, managing inventory, and marketing their services.
Ethical Considerations: To emphasize the importance of ethical conduct, data privacy, and respecting customer confidentiality.
Quality Control: To stress the significance of quality control and ensuring that repaired phones meet industry standards.
Adaptation to Technological Advances: To encourage students to stay updated with the ever-evolving mobile technology and adapt to new trends and innovations in the field.
Problem-Solving Skills: To enhance problem-solving abilities, as each phone repair may present unique challenges that require creative solutions.
Entrepreneurship: For those interested in starting their own phone repair business, the course may also aim to provide the knowledge and skills required to run a successful entrepreneurial venture in this field.
Course Content
INTRODUCTION TO MOBILE PHONES AND SERVICE PROVIDERS
- Mobile phones acronyms and terminologies
- Mobile phone bands and their uses
- Types of mobile phones
- Phone accessories and their functions
- Types of menus and sub-menus
ESSENTIAL COMPONENTS OF MOBILE PHONES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
- Structure of mobile phones
- Hardware components
- Software components
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR OF MOBILE PHONES
- Electronic components in mobile phones
- Preventive maintenance
- Corrective maintenance
- Common tools and equipment for hardware and software repairs.
- Safety in mobile phone workshop
- Common hardware problems
- Common software problems
TROUBLE-SHOOTING
- Basic trouble-shooting
- Tracing and fault finding in hardware
- Fault finding in software
SETTING UP AND MANAGING MOBILE PHONE WORKSHOP
- Setting up a mobile phone work shop
- Facilities/equipment for mobile phone workshop.
- Managing a mobile phone business
- Carrier opportunities
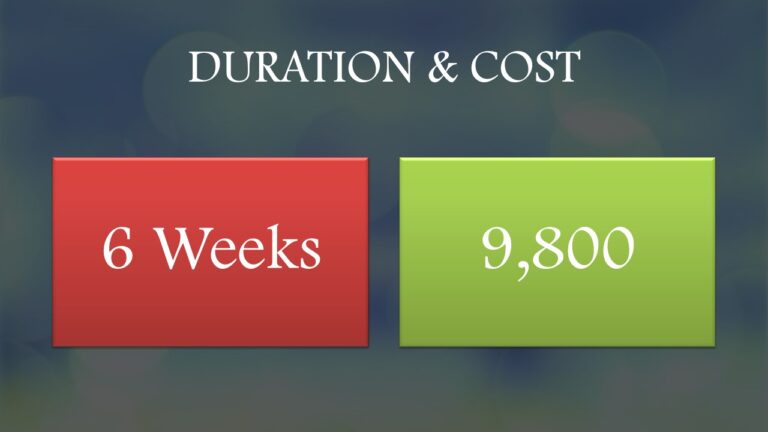
COMPUTER REPAIRS
Objectives
Identify Hardware Components: By the end of the course, students will be able to visually identify and label major hardware components inside a computer, including the CPU, motherboard, RAM, and hard drive.
Diagnose Hardware Issues: Students will demonstrate the ability to diagnose common hardware problems, such as overheating, power supply failures, and faulty RAM, by utilizing diagnostic tools and methods.
Assemble and Disassemble Computers: Upon completing the course, students will successfully assemble and disassemble a desktop computer, showcasing proper handling and organization of components.
Perform Operating System Installation: Students will install and configure operating systems (e.g., Windows, Linux) on a computer, ensuring that drivers and necessary software are properly installed.
Virus and Malware Removal: After the course, students will be able to detect and remove viruses and malware from a computer system while preserving user data and system functionality.
Data Backup and Recovery: Students will demonstrate the ability to perform data backups and execute data recovery procedures, ensuring minimal data loss in case of hardware failures.
Troubleshoot Network Issues: By the course’s end, students will be able to troubleshoot common network connectivity issues, including configuring routers, switches, and resolving IP address conflicts.
Customer Interaction: Students will exhibit effective communication and interpersonal skills when dealing with customers, explaining technical issues in a clear and understandable manner.
Adherence to Safety Practices: After completing the course, students will consistently follow safety protocols and best practices, such as ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) prevention and safe handling of computer components.
Documentation and Reporting: Students will maintain comprehensive repair records and generate clear reports detailing the issues identified, repairs conducted, and parts replaced.
Up-to-Date Knowledge: Graduates will exhibit a commitment to staying current with industry trends and technologies in computer repair and maintenance.
Quality Assurance: Students will adhere to quality control standards, ensuring that repaired computers meet or exceed industry and manufacturer specifications.
Time Management: Students will efficiently manage their time to diagnose and repair computer issues within reasonable time frames, minimizing downtime for customers.
Course Content
Module 1: Introduction to Computer Hardware
- Understanding computer components and their functions
- Differentiating between desktop and laptop hardware
- Tools and equipment used in computer repair
Module 2: Computer Assembly and Disassembly
- Proper handling of computer components
- Step-by-step assembly and disassembly of a desktop computer
- Assembling and disassembling laptop components
Module 3: Hardware Troubleshooting
- Diagnostic techniques for common hardware problems
- Identifying and replacing faulty components (e.g., RAM, hard drive, power supply)
- Preventative maintenance and cleaning
Module 4: Operating System Installation and Configuration
- Installing Windows and Linux operating systems
- Driver installation and updates
- Configuring the operating system for optimal performance
Module 5: Software Troubleshooting
- Identifying and removing viruses, malware, and unwanted software
- Software updates and optimization
- Data backup and recovery methods
Module 6: Network Troubleshooting
- Basic networking concepts
- Diagnosing network connectivity issues
- Configuring routers and switches
Module 7: Customer Service and Communication
- Effective communication with customers
- Customer needs assessment and problem explanation
- Handling customer concerns and inquiries
Module 8: Safety and ESD Practices
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) prevention and safety protocols
- Safe handling of computer components
- Fire and electrical safety
Module 9: Documentation and Reporting
- Keeping repair records and documentation
- Preparing repair reports and invoices
- Legal and ethical considerations in record-keeping
Module 10: Industry Trends and Professional Development
- Staying updated with the latest computer technologies
- Continuing education and certification options
- Building a career in computer repair and IT support
Assessment and Practical Labs:
- Hands-on practical exercises and labs for hardware and software troubleshooting
- Quizzes and assignments to evaluate knowledge retention
- Final repair projects on real-world computer issues
Certification: Participants who successfully complete the course and demonstrate competency will receive a certificate in Computer Repair.


